- Battery-short notes
- Types of marine batteries
- Starting or cranking batteries
- Dual-purpose batteries
- Deep cycle battery
- Type of deep cycle batteries
- Flooded deep cycle battery
- Sealed or maintenance free battery
- What is the difference between starting batteries and deep cycle batteries?
- What does CCA mean?
- What are CA and MCA?
- What are the parts of the battery?
- What are the alarms and indications on battery charger panel?
- What is Electrolysis?
- EMF, Potential difference, and Internal Resistance of battery
- Battery charging methods
- What are the types of charging a battery?
- What is Initial and Normal Charge?
- What is Float or Trickle Charge?
- What is Quick Charge?
- What is Equalizing or Special Charge?
- What are the Indications of a fully charged battery?
- What happens if I keep on charging a lead-acid battery after it’s fully charged?
- What are the problems arising in the Lead Acid Batteries?
- Battery – Application in a ship
- What are the 24 VDC Services on a ship?
- Hazards Associated With Marine Batteries
- Electrical Safety Precautions
- Handling Battery Acid
- PPE Requirements for Electrolyte Handling
- Battery Life
- What are the precautions during cleaning the battery?
- Battery maintenance (LEAD ACID BATTERIES)
- Lead-acid battery maintenance procedure
- 1.Weekly check
- VRLA (Valve Regulated Lead Acid Battery) Maintenance-free batteries specific additional instructions:
- 2.Monthly check
- 3.Three monthly check
- 4.Annual check
- Safe operation and maintenance of VRLA lead-acid batteries
- Maintenance of engine starter batteries and the starter circuit
- 1.Weekly check
- 2.Monthly check
- 3.Annual check
- What are the requirements as per SOLAS for the GMDSS battery?
- Battery and battery room regulations as per SOLAS
- Ship battery room PPE requirements
- Why is the negative terminal of a battery disconnected first and connected last?
- Why positive terminal of the battery is not grounded?
- Why we use petroleum jelly, not grease for terminal corrosion protection in battery?
- What is the difference between nickel-cadmium and lead-acid batteries?
- How we can order battery on-board?
- What is transitional batteries and their duration?
- Battery capacity test how to do?
- What is the Battery renewal duration for GMDSS?
- Why do not keeping alkaline battery and lead-acid battery in the same compartment?
- What is the charging current for 200 Ah battery?
- Most commonly used batteries on the ship
- How to do the battery load test
- What is the difference between GMDSS and GENERAL battery?
- What is the method of lifeboat battery charging?
- Why lifeboat battery charging voltage is specifically 42VAC not 220VAC?
- Can we did the battery Megger test?
- Alkaline battery (Primary) size code
Battery-short notes
- A cell is a device for converting chemical energy and accumulate it in the formation of electrical energy by a process called electrolysis. Included an anode, a cathode, and an electrolyte.
- A cell possibly a Primary cell or a Secondary cell.
- A primary cell has an irreversible chemical action and can’t be recharged once completely discharged.
- A secondary cell can be recharged for several cycles of charge and discharge.
- A group of cell (one or more cells) is called a battery.
Types of marine batteries
Generally, there are three types
- Starting or cranking batteries
- Dual-purpose batteries
- Deep cycle batteries
Starting or cranking batteries
These batteries are designed to discharge a huge amount of
energy short period
Dual-purpose batteries
These batteries are can be used as stating battery or deep
cycling battery.
Deep cycle battery
A deep-cycle battery is made for maximal energy storage
capacity and high cycle count or long life and run reliably until it is 80
percentage discharged or more. This is obtained by placed thick lead plates
with the limited surface area. Generally used in UPS and marine applications.
Type of deep cycle batteries
There are different types. Generally, two common types are
using in marine applications.
- Flooded deep cycle battery
- Sealed or maintenance-free deep cycle battery
Flooded deep cycle battery
- Its require regular monitoring
- To maintain the good performance of this type of battery should refill the battery when the electrolyte levels are low
Sealed or maintenance free battery
- These batteries are also called valve regulated lead acid batteries.
- Regular inspection is required for maintaining the best performance.
- No need to refill
What is the difference between starting batteries and deep cycle batteries?
- Starting batteries: discharge a huge amount of energy in short duration
- Deep cycle batteries: discharge a small amount of energy in long duration
What does CCA mean?
CCA – cold-cranking amps
Generally, it is used to determine a battery's capability to
start an engine in cold temperatures. The amount of amps a lead-acid battery
can deliver at 0 degrees F for 30 sec, while still keep terminal voltage
equivalent to or higher than 1.2 volts per cell.
What are CA and MCA?
CA: cranking amps
MCA: Marine cranking amps: The amount of amps a lead-acid
battery can deliver at 32 degrees F in 30 sec
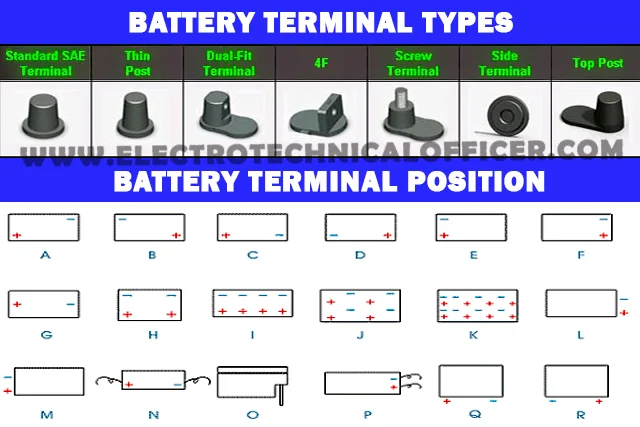
What are the parts of the battery?
Main
component parts shall be as follows
PARTS
|
MATERIAL
|
Positive plate
|
Pasted type with
lead-calcium
|
separator
|
Glass fiber mat
|
Container and cover
|
Flame retardant ABS
resin
|
Safety valve
|
rubber
|
connectors
|
Lead coating copper
plate
|
What are the alarms and indications on battery charger panel?
- Input power fail (setting point: 50sec)
- Earth leakage (setting point: 5k)
- Over current
- Output under voltage (setting point: 22v)
- Output over voltage (setting point: 31v)
What is Electrolysis?
Electrolysis
is a process of using an electric current to drive a chemical reaction
resulting in the separation of materials.
EMF, Potential difference, and Internal Resistance of battery
The
electromotive force (EMF) of a cell is the potential difference between the
positive and negative plates of a cell on open circuit and is denoted by “E”
Potential
Difference or Terminal voltage of the cell is the potential difference between
the plates of a cell when delivering current to the external circuit and is
denoted by “V”
Internal Resistance: The
opposition offered to the flow of current in a cell is called the Internal
Resistance of the cell and is represented by “r”. The internal resistance of
the cell is due to Electrodes, electrolytes, and the terminals of the cell.
Battery charging methods
Charging -
The operation carried out to revoke the discharged condition of a battery
A source of
DC supply is required.
Constant
current method – The charging current is kept constant by regulating the
external resistance, the method being appropriated only for the initial
charging of the battery.
Constant
voltage method – The charging voltage is maintained constant. The charging
current is high at the start however slowly reduces as the battery voltage
builds up.
Constant voltage charge method is the most common method of charging
What are the types of charging a battery?
According
to the condition of a battery, the following types of charges possibly given to
a battery
- Initial Charge
- Normal charge
- Floating charge or Trickle Charge
- Quick charge
- Equalizing charge
What is Initial and Normal Charge?
Initial
Charge: An extensive low-rate initial charge given to a brand new battery
following the initial filling of electrolyte, the voltage/current rate, and
charging time stated by the maker.
Normal
charge: the standard charge given as per manufacturer data during the usual
cycle of operation
What is Float or Trickle Charge?
The rate is
set on by the battery voltage. A trickle charge manages to retain the battery
at full charge while the battery is idle or on light load and it is done by the
low current. Kept the voltage of the charging source is slightly higher than
the battery voltage to obtain the preferred current
What is Quick Charge?
Quick
charge is given when a battery should be recharged within the shortest time
duration, the charge starts at a considerably higher rate than the usual rate.
This type of charge is to be used only in an emergency situation and a quick
charge could damage the battery.
What is Equalizing or Special Charge?
The special
enhanced ordinary charge that is occasionally given as part of the maintenance
routine. It makes sure that all sulfate is moved from the plates and that all
the cells are put back to the greatest value of specific-gravity. The charge is
continued until the Specific-gravity of all the cells show no vary for a
four-hour period
What are the Indications of a fully charged battery?
During charging: it should take less current
compare no normal charging current level.
Idle condition:
For 12V battery - Terminal voltage above or equal to 12.6V or equal to
about the maximum charging voltage. And cell voltage becomes constant.
Best way: Measure the electrolyte with the help of a hydrometer. The specific gravity is 1.265 when fully charged for most common
batteries
What happens if I keep on charging a lead-acid battery after it’s fully charged?
- Lifetime will be reducing and perhaps even damage the battery.
- Storing current will be more and hydrogen gas come out the form of a battery explosion due to electrolysis reaction.
What are the problems arising in the Lead Acid Batteries?
- Loss of Electrolyte – Due to high temperature, charging rates high and overcharging
- Sulphation – Generally noticed by whitish color on the plates and is effected by overcharging, over-discharging and kept the battery in a discharged condition for a long time.
- Stratification of electrolyte – Due to battery is not fully charged
- Failure of Separator – Due to excessive heat and overcharging
- Fully Discharge
Battery – Application in a ship
A Battery
Power Pack is used as a TRANSITIONAL SOURCE OF POWER to supply the Emergency
loads during the
- Change-over from main power to the Emergency source of power
- When both the emergency and main power are a failure.
- Emergency lighting, navigation equipment’s, telecommunication equipment’s, etc. of ship
What are the 24 VDC Services on a ship?
- Engine Control Systems
- Bridge control console
- Public address
- Elevator control unit
- Navigation light control and indication
- Fan control for cargo hold
- Auto telephone exchanger
- Gyrocompass
- Autopilot terminal unit
- Magnetic compass interface and dimmer unit
- Master clock
- Echo sounder interface and printer unit
- Speed log
- AIS
- Ship security alarm system-SSAS
- BNWAS
- Whistle signal controller
Hazards Associated With Marine Batteries
- Hydrogen Gas (a by-product of the battery charging process, lighter than air, flammable in nature, explosive mixture at 4 to 74 percentage by volume of air, and you can smell the acid in the battery if it heats up )
- Sulphuric Acid (corrosive material, burns to skin, burns to eyes, and never open the battery caps with your face directly over the battery)
- Electrical (short circuit the terminal by accident)
- Weight of the Battery (The battery is heavy, appropriate use of transport, handling to be careful to avoid a collision, when installation; pay attention to safety)
Electrical Safety Precautions
- Please be sure to according to the company and maker instructions.
- Please wear safety glasses, wear appropriate clothes, completes the accident prevention work.
- Smoking is prohibited, eliminate all fire, explosion, and fire risk.
- Avoid short circuits that cause fire and explosion danger.
- Don’t touch both battery terminals with your plain hands at the same time.
- Remove rings, watches, and dangling jewelry when working with or near batteries. The metal in the jewelry can cause a shock or burn if they contact the battery terminals.
- Use only insulated tools to remove cell caps. Not at all place the tools or other metal parts on the battery.
- Consider covering battery terminals and connectors if possible with an insulating blanket before overhead inspections or repairs
- Ensure charger is turned off before connecting or disconnecting a battery to prevent arcing
Handling Battery Acid
- Always wear proper eye, face, and hand protection.
- Use non-metallic containers to handle liquid
- If the electrolyte is splashed into an eye, please rinse immediately with plenty of water, and promptly consult a medical team.
- To compose the electrolyte of a required specific gravity, at all times pour the concentrated acid gradually into the water; don’t pour the water into the acid directly. If detectable heat generates let the solution to cool prior to keeping to add acid.
PPE Requirements for Electrolyte Handling
- Safety Glasses/goggles
- Rubber Gloves
- Face Shield
- Chemical suit
- Safety shoes
Battery Life
500 to 800 charge-discharge cycles = 3 years of battery life
on average
When the battery is starting to die the battery power starts
to decrease
A charged battery will start to lose its energy if not used
The battery power depends on how the equipment is made
What are the precautions during cleaning the battery?
- Use wet cloth (dry cloth [especially chemical fiber] produce static energy and cause dangerous)
- Do not use the organic solvent such as gasoline, also do not use containing these substances cloth wipe the battery.
Battery maintenance (LEAD ACID BATTERIES)
The following checks should be carried out daily:
Battery charging voltage should be checked.
The insulation level by earth lamps or megger meter at the
Battery Charger unit.
All batteries should
be renewed every 2 to 3 years or earlier if required.
At 48.9°C batteries floating charge should be ceased and
battery charged only as required to maintain full charge till the ambient
reduces and it can be placed on float charge as usual.
Life Boat / Rescue Boat batteries and chargers are liable to
damage in extremely hot ambient conditions.
Lead-acid battery maintenance procedure
Carry out the following maintenance procedure for the ship’s
Emergency Battery/ GMDSS Battery to ensure, good working conditions.
1.Weekly check
- Examine the outside appearance of the battery. Check for bulging and deformation.
- Check the container for cracks. This can lead to external short-circuiting /earthing.
- Check the top of the battery, the posts & connections should be clean, free of dirt, fluids, corrosion and apply petroleum jelly on the terminals to prevent corrosion. Ensure vents are clear.
- Check the specific gravity, voltage, negative terminal temperature for each individual cell, and ambient temperature around the batteries and record. The temperature correction for voltage and specific gravity to be applied and recorded.
- The temperature will affect specific gravity readings. Check the specific gravity of all the individual cells in the battery on a floating charge. Ensure the temperature correcting factor is applied for specific gravity readings to 26.7°C. Add 0.004 to readings for every 5.5°C above 26.7°C and subtract 0.004 for every 5.5°C below 26.7°C.
- The temperature will affect voltage readings. For every 5.5°C below 26.7°C add 0.028V per cell and subtract 0.028V per cell for every 5.5°C above 26.7°C.
- Make sure the Charger voltage and current on the charging panel as per maker instruction.
- Check the batteries are secured properly on wood / suitable storage facilities and well ventilated.
- Check the electrolyte level of all batteries. Do not top-up distilled water to the maximum if the battery is not fully charged. Final topping up to be carried out when in a fully charged condition.
- Batteries with transparent body casing should be closely examined with a safety flashlight for sulfated plates and large deposits at the bottom of the battery which is a strong sign of deterioration and could short circuit the cell.
- Strong rotten egg smell of H2S is an indication of the battery gassing up due to overcharging.
VRLA (Valve Regulated Lead Acid Battery) Maintenance-free batteries specific additional instructions:
- Any sign of fluid or stains on the top of the cell if not due to external reason indicates that the safety relief valve may be leaking or has lifted.
- This indicates a loss of hydrogen and the cell needs to be monitored and replaced as the electrolyte level cannot be checked due batteries are sealed and AGM type (or GEL).
- The provision of a green indicator that is common for the deep-cycle starter batteries will only provide the specific gravity in range for one cell and not the other cells.
- There is no provision to check the specific gravity as the battery is sealed.
2.Monthly check
- Carry out the weekly check as listed and analyze the condition of the battery over the month. Check if any individual cells are deteriorating (voltage drop, specific gravity drop, and rise in temperature at the negative terminal.)
- After all the cells are confirmed to be fully charged and on float charge for at least 6 hours carry out “ equalizing charge “for twenty minutes and switch back to the floating charge.
- Voltage, the temperature at the negative terminal, and specific gravity to be checked within limits. This helps to keep the plates at full charge, ensures the electrolyte is uniform and free of stratification.
3.Three monthly check
- Switch off the charger and discharge the battery to 50% for minimum of 6 hours information to record:
- Overall float voltage and current of the string before the start of discharge (with the charger on)
- The float voltage of each cell before the start of discharge (with the charger on)
- Record the temperature of the electrolyte of 10% or more cells to establish an average temperature.
- Record the temperature at the negative terminal of each cell and ambient temperature.
- At regular intervals (every hour) check Total DC voltages, Amperage and individual cell voltage.
- As the test nears its end monitors the voltage for each cell at closer intervals and stop the discharge if any cell approaches the minimum voltage as specified by the maker.
- A lead-acid 2V cell end of discharge minimum voltage is 1.75V. The battery must never be over-discharged to exceed 80% of the Ampere-hour (Ah) capacity.
- On completion of the discharge, the battery must be placed on the charging cycle. Once the battery is fully charged the monthly check to be carried out.
- Do not leave the batteries in a state of discharge for a long period. This will cause hard sulfate formation on the plates with a reduction of battery capacity, high amperage being absorbed on the active part of the plates, gassing up, and possible thermal runaway.
- Important: If replacing lead acid with alkaline batteries follow the maker’s instructions.
4.Annual check
- Batteries must never be drained 100%. The maximum safe discharge is 80%, exceeding this may damage the battery and the battery charger.
- During discharge test individual cell voltage should not be allowed to fall below the minimum voltage rating.
- The load test to be carried out as per the 3 monthly check and to be stopped when the cell minimum voltage is reached (1.75V for a 2V cell) at approx. 80% discharge and results to be estimated.
- If any individual cell reaches the minimum voltage pre-maturely, it will need to be replaced before continuing the test on the remaining healthy cells in the battery bank.
To calculate the % capacity of your system:
Estimated capacity at 25°C
C % = Ta x 100
Ts x Kt
Ta = The actual time in minutes of the test to the specified end
voltage
Kt = The time correction factor in below table
Ts = the rated time in minutes of the test to the specified
end voltage
Temperature
degree
Celsius
|
Kt value
|
20.5
|
0.968
|
21.1
|
0.955
|
21.6
|
0.960
|
22.7
|
0.975
|
23.8
|
0.985
|
25.0
|
1.0
|
26.1
|
1.007
|
26.6
|
1.011
|
27.2
|
1.017
|
28.3
|
1.030
|
29.4
|
1.040
|
30.5
|
1.050
|
31.6
|
1.06
|
32.2
|
1.065
|
Example: A 2 V - 220 Ah Battery is rated to deliver 38Amps
for 5 hours (300mins) to 1.75V DC at 25°C. The system was at 23.8°C was
discharged at 38Amps and the system end voltage was reached at 4 hours and 25
minutes (265mins).
C% = 265mins x 100 = System has 89.67% capacity.
300mins x 0.985 = 295.5 minutes
When ordering deep cycle batteries, please ensure that the
rated time in minutes to the specified end voltage is requested from the
supplier.
For example, this may be stated as “100Ah battery providing
12.5Amps for 8 hours to 1.75V per cell.”
Safe operation and maintenance of VRLA lead-acid batteries
- Thermal runaway: This is the primary cause of major battery failure and damage. During float charging of a VRLA battery, 90% of the current supplied is used to facilitate the oxygen recombination cycle.
- Batteries generate a fair amount of internal heat. This increases the battery's ability to absorb charging current without a rise in voltage which effectively disables any voltage regulator on the charging device, resulting in gross overcharging.
- Thermal runaway soaks up all the charging current converting this into hydrogen-oxygen and heat.
- Stains on the battery top indicate lifting of the relief valve with loss of hydrogen and oxygen. The loss will lead to exposure of the plate tops with a possible short circuit thus providing an ignition source and also loss of capacity. This is an indication of overpressure, gassing up, and potential thermal runaway.
- A rise in temperature at the negative terminal 10°C above ambient will indicate a potential runaway / gassing up of the battery.
- Cracks on battery containers lead to leakage with grounding and possible short circuits.
- Battery Charger to be in good order and suitable for the charging of the VRLA lead-acid battery in all modes boost/float / equalizing. The voltage should always be within the parameters for the ambient temperature conditions.
- Stratification with sulfated plates reduces the active area thus leading to thermal runaway.
- Approx. voltage table for cyclic use charging. The higher voltages (above the gassing voltage) should only be used on flooded batteries that can have the water replaced after direct venting to the atmosphere.
Maintenance of engine starter batteries and the starter circuit
- Engine Starter Batteries use the top 20% of the battery or less and then is to be re-charged. Their design can provide a lot of power for a short period unlike the deep cycle emergency battery bank which can provide power for a long period and discharge to 80% of the battery.
- Starter Batteries are used for Emergency Generator engines, Rescue Boat engines, and Life Boat engines.
- The battery temperature is critical and batteries exposed to the outside heat (Life Boats) may have their electrolyte temperature soar to above 48.9°C in which case the Battery Charger should be switched off and charge to be maintained by manual use till such time that the ambient condition improves to an acceptable level. This will prevent thermal runaway and damage to the batteries and chargers.
1.Weekly check
- Weekly check to included the starting of the engine by each battery individually along with the checks as per 13.4.2.1.
- Monitor the area of operation and if the high ambient temperature is expected action to be taken to prevent overcharging and exceeding the electrolyte temperature limit of 48.9°C.
2.Monthly check
- Monthly check to include the starting of the engine by each battery individually along with the checks as per 13.4.2.2.
- Each individual Starter Battery to be tested by starting the engine thrice. The end voltage to be checked on the conclusion and should not be below the recommended minimum voltage. Cranking of the engine should be healthy without a sluggish response.
- 3 monthly check to be carried out as per 13.4.2.2 as applicable.
- The Starter Batteries should be tested and the voltage dip measured across the terminal during the cranking process. The result to be recorded. A large dip may indicate a dying battery or bad connections.
- The charging amperage/voltage from the alternator to be recorded
3.Annual check
- Annual test to include a proper check of the Starting Circuit and the Starter.
- Spare Starter Motor to be checked in good order.
- The voltage drop test is the only effective way to detect excessive resistance in high amperage circuits.
- Voltage drop check for the Starter Circuit:
- Disable the engine so it cannot be started when cranked. Limit cranking time to 10 sec.
- While cranking the engine, check the voltage across the battery terminal studs.
- While cranking the engine, check the voltage across the positive terminal of the battery and the starter housing.
- Compare the readings. If both are the same then there is no excessive voltage drop on the positive feed side. If the available voltage on the starter side is not within 1.5V of the battery voltage then the voltage drop is excessive.
- Make sure the battery is fully charged. Measure the voltage across the positive terminal of the battery and the negative battery stud on the starter (use the 2V scale) while cranking the engine the maximum voltage drop should be 0.8V or less for the positive side of the Starter Circuit.
- While cranking the engine measure the voltage across the starter case and the battery post. A good connection will give a voltage drop of 0.4V or less for the negative side.
- The Starter Motor to be removed and moving contacts / fixed contacts to be cleaned all parts to be checked for corrosion. The Solenoid to be cleaned and checked for corrosion.
- The Alternator Belt to be checked for tightness and good condition. The charging function to be checked.
- Hazardous nature of batteries require disposal to conform to MARPOL garbage requirements.
What are the requirements as per SOLAS for the GMDSS battery?
The requirement of GMDSS batteries is governed by Part-C,
Regulation 13, and Chapter 4 of SOLAS.
- 6.1 The batteries should be recharged to the required minimum capacity in less than 10 hours
- 6.2 the capacity of the batteries should be checked, using an appropriate method at intervals not exceeding 12 months, when the ship is not at sea.
Battery and battery room regulations as per SOLAS
The requirement of batteries is governed by Part-D, Regulation
43, and Chapter 2-1 of SOLAS.
- It should be automatically connecting to ESB (Emergency Switch Board) when the main power source fails.
- Immediately supply power to minimum services specified for emergency sources.
- The battery should not discharge more than 12% of the nominal voltage.
- The battery room is designed in such a way that it will prevent spillage of electrolyte & emission spray.
- The battery room should be painted with an acid-resistant paint.
- Battery room floor should be Anti-acidic floor
- Should be an independent exhaust fan provided. Inlet-duct should be below battery level, and outlet should be fitted at top of the compartment
- Battery room lighting should be installed with Exd proof
- Make sure the proper illumination in the room
- Should be posted No smoking, No naked lights, and playing cards.
Ship battery room PPE requirements
Kept the separate PPE for battery room operations
- Eye protection (goggles)
- Corrosive resistant gloves
- HV insulated gloves
- Corrosive resistant apron
- Eyewash
Why is the negative terminal of a battery disconnected first and connected last?
The system is having negative terminal grounded always.
So even if you accidentally touch negative terminal to the
hull or metal part of the structure, nothing will happen. But if positive
touches the negative or ground there are a spark and the system may get
damaged.
Why positive terminal of the battery is not grounded?
For easier to analyze positive signals.
Why we use petroleum jelly, not grease for terminal corrosion protection in battery?
When the terminal will get heated grease may melt and comes
out and exposed the terminal again for oxidation. And grease contains oil so
chances of fire hazard in case of sparks.
What is the difference between nickel-cadmium and lead-acid batteries?
The main difference is specific gravity does not change in
nickel-cadmium battery at charging and discharging condition
PROPERTIES
|
NICKEL CADMIUM BATTERY
|
LEAD ACID BATTERY
|
Positive
|
Nickel hydroxide + graphite
|
Lead peroxide
|
Negative
|
Cadmium + iron
|
Spongy lead
|
Electrolyte
|
Potassium hydroxide solution
|
Sulphuric Acid (H2SO4)
|
Specific gravity
|
1.21 and does not change
www.electrotechnicalofficer.com
|
Fully charged: 1.265 @80° F
Fully discharged: 1.1
|
Cell voltage
|
Nominal voltage is 2V
|
Nominal voltage is 1.2V
|
Efficiency
|
Moderate
|
Higher
|
Cost
|
High Cost
|
Low Cost
|
How we can order battery on-board?
We have to mention the following things when ordering the battery
- Type of battery
- Battery capacity
- Maintenance-free battery or normal
- Type of terminal
- Terminal position
- Voltage rating
- Dimensions
- CCA and MCA
What is transitional batteries and their duration?
Transition batteries supply power to emergency lights,
fire control, internal communication, etc. before the emergency gen comes on
load just after the blackout and is supposed to give power for at least 30
mints
Battery capacity test how to do?
With the approved load tester.
The load tester will have FLC marked on it. And we are aware
of capacity so we will calculate the discharging time. Before connecting load
tester we will check the terminal voltage and afterload testing also we will
check the terminal voltage it should not have a drop of more than 12% of rated
voltage
What is the Battery renewal duration for GMDSS?
It depends on the maker's instructions, usually, it is 3/5/7 year’s
cycle.
30 months for maintenance-free batteries.
Why do not keeping alkaline battery and lead-acid battery in the same compartment?
The alkaline battery cells will be become contaminated by
acid vapor (fumes) causing permanent damage.
Note: Do not use the same tools for different types of battery.
Because slightest traces of acid can cause serious damage to alkaline cells.
What is the charging current for 200 Ah battery?
T = Ah / A
Where,
T = charging time
Ah = Battery capacity
A = Charging current
20 A
As SOLAS regulation says batteries should be chargeable in
10hrs
Most commonly used batteries on the ship
FLOODED BATTERY
|
|
SEALED BATTERY
|
|
VRLA BATTERY
|
|
AGM BATTERY
|
|
How to do the battery load test
- Before switching off the main and emergency supply note the voltage at the battery terminal.
- Switch off the main as well as an emergency source of power to the equipment, and also to the battery charger circuit.
- Calculate the deliver current by the means of the voltage and power to be delivered, and divide it by the total AH that battery will deliver. So that you will get the discharge time.
- Keep it monitoring for that period of time, and also note the value of the voltage and ampere periodically.
- If the battery voltage is discharging below 12% of the rated value then you need to change it.
What is the difference between GMDSS and GENERAL battery?
GMDSS battery should give 1-hour power if emergency charging the source is available otherwise gives 6 hours power
General battery should give 30 min backup
What is the method of lifeboat battery charging?
It's on trickle charge, battery charges at a rate of self-discharging
rate
Why lifeboat battery charging voltage is specifically 42VAC not 220VAC?
- Below 50 v is very low voltage, so that voltage doesn't affect the human body
- So for safety reason it 42 vac
- In case of an emergency, we can remove the charging plug without switching off the supply
- If you use 220VAC we need to accommodate then separate battery charger for batteries inside the boat which is not feasible.
- It will be then declared as the unsafe area on LPG, oil tankers if the voltage is high which can be hazardous in terms of spark and fire.
- Safe working voltage as said earlier can be removed or unplugged without switching off the breaker too.
Can we did the battery Megger test?
No, we are never supposed to do meggering on live batteries
that too connected on load, more specifically never megger on terminals of the battery.
















6 Comments
Complete battery material thanks Maniknandan 👍
ReplyDeleteTransformer ouput should be connected to anode and cathode junction of bridge rectifier please correct it
ReplyDeleteThank you for your information dear and corrected!
DeleteCan any of the ETOs/Marine Engineers answer that how does changeover mechanism of UPS from Main Power Supply to Battery Power Supply [12V DC or 24V DC or 110V AC or 220V AC]? Though we know that the changeover time for any or all computerized system or micro-controller exceeds more than 19 milli seconds that system will shut down and has to be re-started. In general the UPS available in the global market takes between 03 milli seconds to 08 milli seconds [ some models take upto 14 milli seconds]. Standard INVERTERS take 2 to 5 seconds to changeover power supply from mains to Inverter which is much more than 19 milli seconds, therefore COMPUTERIZED System shut down before Inverter takes over the loan.
ReplyDeleteThnks & Regards,
Dr. Mukesh Kumar
Ex-ETO
BSM
MUKESH63.K@GMAIL.COM
UPS takes about 5ms to transfer which means there will be no output for about 5ms from the power failure to the Inverter taking over. If you have a computer connected then that computer’s power supply itself will power the system for that 5ms period, main bulk capacitor is in charge of doing it. There is a standard, which is ATX power supplies have to have 16ms hold up time but some power supplies have less than that some have more, depending on the capacitor and power supply capacity.
DeleteThank yyou for sharing
ReplyDeleteWe love to hear your comments on this article, so that we may better serve you in the future.